What does a tension headache feel like?
People commonly describe tension headaches as feeling like a tight band is wrapped around their head. Familiar with that uncomfortable sensation? Tension headaches may also present with:2
Constant, dull head pain on both sides of the head
Mild to moderate (but not severe) aching in the head
Tightness or pressure across or around the head
Stiff neck or shoulder muscles, along with tenderness in the scalp
Tiredness, irritability, or difficulty focusing
What are the different types of tension headaches?
There are generally 2 main types of tension headaches.3 These ‘types’ are characterized by frequency:
Episodic tension-type headaches. You fall into this category if you experience less than 15 headache days a month.
Chronic tension-type headaches. This is when the number of days you have headaches outnumber the days you don’t have headaches. It’s considered chronic when you experience 15 or more headache days a month for more than 3 consecutive months.
Headaches can last anywhere between 30 minutes to several days. Fortunately, while you may dread getting these nasty headaches, they are not generally considered to be dangerous.
What causes a tension headache?
The exact cause of a tension headache remains unknown.4 Researchers believe genetics and environmental factors may play a role. Some triggers that may provoke a headache include:
Emotional stress
Lack of sleep or insomnia
A cold, the flu, or a sinus infection
Fatigue
Anxiety or depression
Skipping meals or dehydration
Pain in the neck or other parts of your head
How to prevent a tension headache?
Living a healthy lifestyle while effectively managing stress may help to prevent headaches.
Lifestyle tips:
Get enough rest. The National Sleep Foundation6 recommends adults to get 7 to 9 hours of sleep every night.
Get adequate physical activity. A healthy adult should get at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise a week.
Eat healthy, balanced meals. Consider using Harvard’s Healthy Eating Plate7 guide to plan your meals.
Stay hydrated. Dehydration can be a trigger for headaches, so make sure to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Quit smoking and limit alcohol. No explanation needed.
Stress-management techniques:
Limit stress. We know, it’s easier said than done. But consider getting a planner or daily checklist to keep your day organized or schedule time (even 10 minutes) during the day to read a blog or watch an episode of Friends.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). One-on-one therapy sessions, like CBT,8 can provide you with a safe outlet to talk about your stress while learning to manage it.
Biofeedback training. Biofeedback9 is a technique you can use to learn how to control certain body responses. During a session, your therapist can connect devices that monitor specific body functions. You can then learn how to manage your body’s response to stress, or even your body’s perception of headache pain.
Relax yourself. Think about what relaxes you. Do you like reading with the sounds of ocean waves playing in the background? Or, perhaps, do you enjoy yoga or meditation? Try to incorporate time to wind down after a long, productive day.
If you have chronic tension headaches that are difficult to manage, your doctor may prescribe preventative medications (usually antidepressants, anticonvulsants, or muscle relaxants) to help reduce the frequency of attacks.
How to treat a tension headache?
Luckily, there are several over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription treatment options available to help reduce headache pain. Some options may be ‘stronger’ than others, so let’s split this up into 3 levels:
Level 1: Pain Relievers. Single-ingredient pain relievers are usually the go-to for mild headache pain. These include:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen
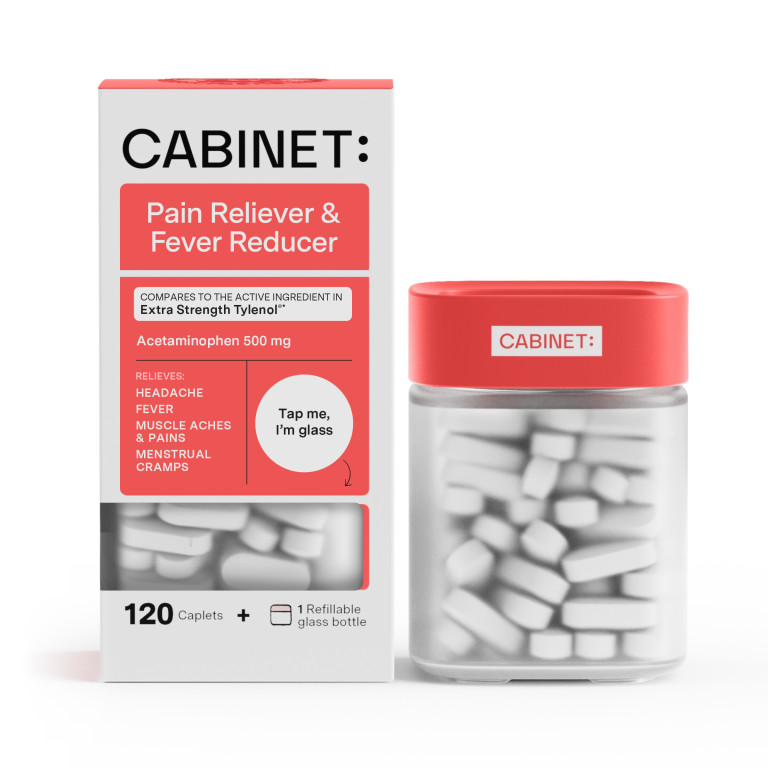
Acetaminophen, available as Pain & Fever Relief
Level 2: Combination pain relievers. The drugs in level 1 are often combined with caffeine or other ingredients to provide more effective headache relief. Some combinations include:
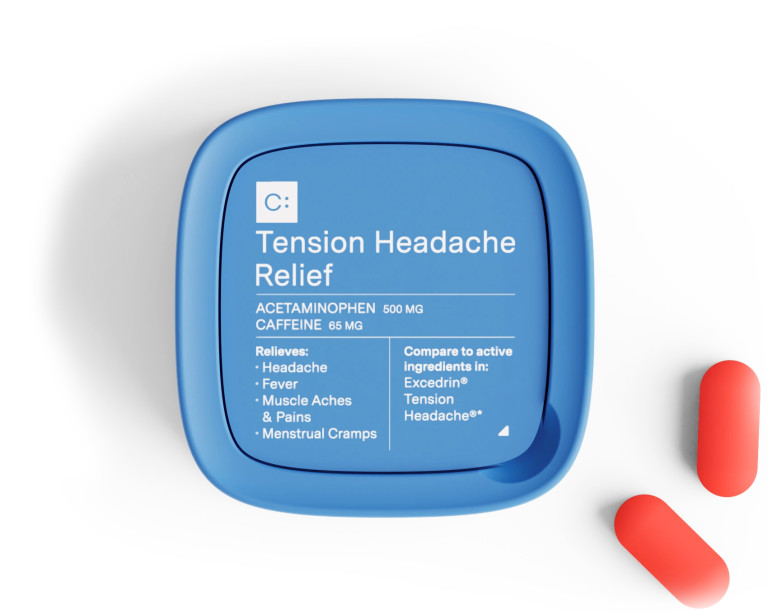
Acetaminophen and caffeine, available as Tension Headache Relief
Acetaminophen and ibuprofen
Acetaminophen, aspirin, and caffeine
Level 3: Prescription medications. People who experience strong episodic tension-type headaches and migraines may be prescribed a triptan10 to relieve pain. Opioids are also an option for pain, but are rarely used due to their side effects and potential for dependency.